1、理论基础
应用场景
- 组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
- 切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
- 子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
- 排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
- 棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
如何理解回溯法
回溯的本质是穷举,穷举所有可能,选出我们想要的答案
回溯法解决的问题都可抽象为树形结构
回溯法解决的问题都是在集合中递归查找子集
集合的大小构成了树的宽度,递归的深度构成树的深度
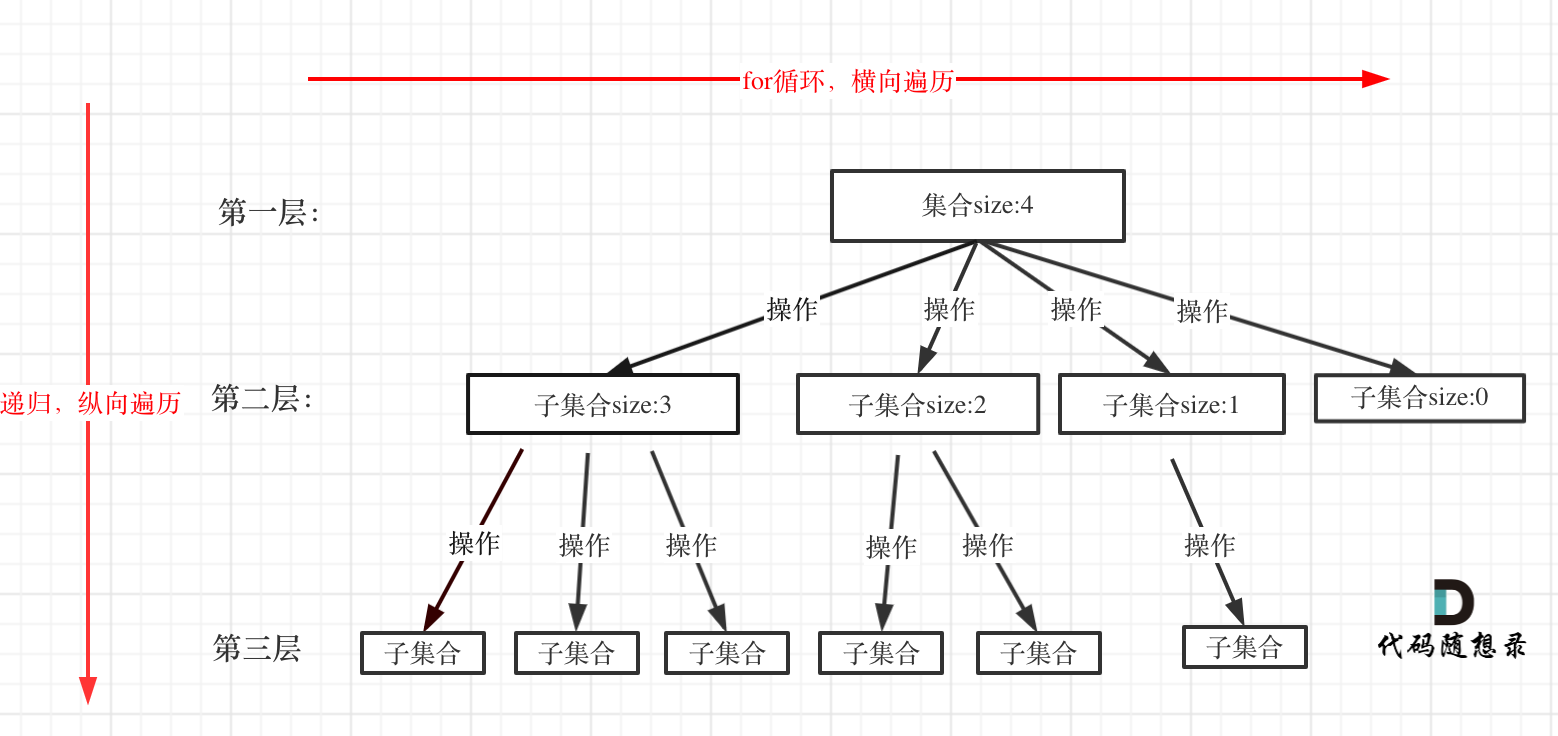
for循环可以理解是横向遍历,backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历
模板:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12void backtrack(参数) {
if (找到一个结果的终止条件) {
存放单次结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
处理节点/处理单次结果;
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
2、lc77-组合
原题链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/
- 回溯法用递归来解决嵌套for循环层数的问题
- 每一次的递归中一个for循环,那么递归就可以用于解决多层嵌套循环的问题
1 | class Solution { |
剪枝优化版
- 如果for循环选择的起始位置之后的元素个数 已经不足 我们需要的元素个数了,那么就没有必要搜索了。
1 | class Solution { |
3、lc46-全排列
组合无序,排列有序
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
- 因为排列问题每次都要从头开始搜索(因为排列是有序的,这样才能得到所有排列的可能),因此可能会遍历到已使用过的元素(一个排列里一个元素只能使用一次)。而 used数组 就是拿来记录此时path里都有哪些元素使用了
1 | class Solution { |
4、lc78-子集
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
- 组合问题和分割问题都是收集树的叶子节点,而子集问题是找树的所有节点
- 无序,取过的元素不会重复取,写回溯算法的时候,for就要从startIndex开始,而不是从0开始
1 | class Solution { |
5、lc17-电话号码的字母组合
- 本题每一个数字代表的是不同集合,也就是求不同集合之间的组合,因此每次递归到下一层遍历都要从头开始(从 0 开始)遍历
1 | class Solution { |
6、lc39-组合总和
- 组合问题:一个集合来求组合的话,就需要startIndex;多个集合取组合,就不用startIndex
- startIndex组合是无序的,虽然本题说明可以重复选取,但最多下一层只能从当前元素的位置开始(往前),绝对是不能从下标 0 开始的(往后重新开始),所以要用到startIndex
1 | class Solution { |
7、lc22-括号生成

- 组合 / 子集 / 排列:同一层可以选择多个不同元素;括号生成:每一层只有两种固定决策:要么
'('要么')',不需要for
1 | class Solution { |
8、lc79-单词搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
1 | class Solution { |
9、lc131-分割回文串
1 | //回溯 + 普通判断回文串 |
1 | //回溯 + 动规判断回文 |
10、lc51-N皇后
https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
- 棋盘的宽度就是for循环的长度,递归的深度就是棋盘的高度
1 | class Solution { |